HeartLung Technologies Sets New Milestone with Nine Accepted Abstracts at AHA 2025 Showcasing the Power of AI-CVD™
I want to congratulate the AI-CVD team for this groundbreaking accomplishment.”
NEW ORLEANS , LA, UNITED STATES, October 21, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- HeartLung Technologies today announced a record-setting presence at the upcoming American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2025, with nine peer-reviewed studies accepted for presentation—spotlighting breakthroughs from the company’s AI-CVD™ platform, including AI-CAC™ and novel CT-derived cardiometabolic imaging biomarkers. The work spans prediction of coronary “soft plaques”, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, COPD, non-zero CAC, and improved detection of aortic disease across the NIH-funded MESA and Framingham cohorts. A key presentation will be HeartLung’s AI-CAC™ — Robert A. Kloner, MD, PhD.
A first-of-its-kind moment for cardiovascular AI.
HeartLung is the only cardiovascular AI company whose papers are cited in the American Heart Association’s official statement on opportunistic screening, and—according to the 2025 program—is the only company ever to have nine abstracts accepted in the history of AHA’s annual Scientific Sessions.
“Across two NIH-funded landmark cohorts—MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) and FHS (Framingham Heart Study)—our AI-CVD research group has achieved truly innovative developments that resulted in all our abstracts being accepted by AHA scientific reviewers,” said Morteza Naghavi, MD, Founder and President of HeartLung Technologies. “These presentations show how AI-derived measurements—of coronary plaques, cardiac chambers, aortic and mitral valves, epicardial fat, and thoracic muscle quality—can meaningfully upgrade preventive cardiology by leveraging millions of chest CT scans done for other reasons.”
“I want to congratulate the AI-CVD team for this groundbreaking accomplishment.” said Robert A. Kloner, MD, PhD, Chief Science Officer; Director and Chair, Cardiovascular Research Institute, Huntington Medical Research Institutes, Pasadena, CA.
Why this matters—now
AI-CVD™ turns a routine CAC scan or a lung scan into a multi-biomarker risk engine: combining AI-CAC™ with valve calcium, aortic metrics, cardiometabolic signatures, and muscle quality (myosteatosis) to deliver a comprehensive personalized risk stratification extremely fast and efficiently. Consistent signals across MESA and Framingham provide a rigorous, peer-reviewed foundation for health systems seeking practical, preventive cardiology that fits existing workflows.
HeartLung presentations at AHA Scientific Sessions 2025
1. AI-driven Measurement of Myosteatosis in Coronary Artery Calcium Scans Predicts Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: An AI-CVD Study within the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4369683
2. AI-enabled Ascending Aorta and Pulmonary Trunk Volumetry in Coronary Artery Calcium Scans for Heart Failure Prediction: An AI-CVD Study within MESA https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4366855
3. AI-Measured Thoracic Ascending Aortic Calcification in CAC Scans Predicts Cardiovascular Events: An AI-CVD study in the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) Offspring Cohort https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4366112
4. AI-driven Aortic Valve Calcification Measurement in Coronary Artery Calcium Scan Detects Aortic Stenosis Comparably to Human Experts: An AI-CVD Study within the Framingham Heart Study https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4355469
5. Artificial Intelligence-Based Coronary Artery Calcium (AI-CAC) Score Empowers the “Power of Zero”: An AI-CVD Study within MESA https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4366401
6. Predicting Non-Zero Coronary Artery Calcium Score in Middle-Aged Population: Comparing an Artificial Intelligence-based Model with Existing ASCVD Risk Scores in MESA https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4366957
7. AI-CVD vs. PREVENT for Predicting Incident Heart Failure: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4366932
8. Identification of High-Risk Cases in Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) Scans Based on CAC Score and AI-driven Cardiometabolic Biomarkers: An AI-CVD Study within MESA https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4371006
9. Artificial Intelligence-Derived Myosteatosis on Coronary Artery Calcium CT Scans Predicts Incident COPD: An AI-CVD Study within MESA https://eppro02.ativ.me/web/index.php?page=Session&project=AHA25&id=4366745
HeartLung AI-CVD™ Coauthors:
Alphabetic Order
Emelia J. Benjamin, MD, ScM — Robert Dawson Evans Distinguished Professor of Medicine; Professor of Epidemiology; Cardiologist at Boston Medical Center, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine and BU School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA.
· Andrea D. Branch, PhD — Professor of Medicine (Division of Liver Diseases); Associate Professor of Surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
· Matthew J. Budoff, MD, FACC, FAHA — Professor of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA; Endowed Chair of Preventive Cardiology & Program Director, Cardiac CT, Harbor-UCLA / The Lundquist Institute, Torrance/Los Angeles, CA, USA.
· Zahi A. Fayad, PhD — Lucy G. Moses Professor of Medical Imaging & Bioengineering; Professor of Radiology & Medicine (Cardiology); Director, Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
· Claudia I. Henschke, MD, PhD — Professor of Radiology; Head, Lung & Cardiac Screening Program, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
· Robert A. Kloner, MD, PhD — Chief Science Officer & Director of Cardiovascular Research, Huntington Medical Research Institutes; Professor of Medicine (Clinical Scholar), Keck School of Medicine of USC, Pasadena/Los Angeles, CA, USA.
· David J. Maron, MD — C.F. Rehnborg Professor of Medicine; Chief, Stanford Prevention Research Center, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
· Michael V. McConnell, MD, MSEE — Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine (and by courtesy, Electrical Engineering & Molecular & Cellular Physiology), Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
· Jeffrey I. Mechanick, MD — Professor of Medicine; Medical Director, Marie-Josée & Henry R. Kravis Center for Cardiovascular Health; Director of Metabolic Support (Endocrinology), Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
· Roxana Mehran, MD — Endowed Mount Sinai Professor in Cardiovascular Clinical Research & Outcomes; Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) and Population Health Science & Policy; Director, Interventional Cardiovascular Research & Clinical Trials, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
· Morteza Naghavi, MD — Founder & President/CEO, HeartLung.AI, Houston, TX, USA.
· Khurram Nasir, MD, MPH, MSc — William A. Zoghbi Centennial Chair in Cardiovascular Health; Chief, Cardiovascular Disease Prevention & Wellness (Houston Methodist); Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, Houston, TX, USA.
· Jagat Narula, MD, PhD — (Current) Executive Vice President & Chief Academic Officer, UTHealth Houston; (Former) Philip J. & Harriet L. Goodhart Chair of Cardiology; Professor of Medicine, Radiology & related disciplines, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Houston, TX / New York, NY, USA.
· Jamal S. Rana, MD, PhD, FACC — Chief of Cardiology, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center; Assistant Physician-in-Chief (Medical Specialties), The Permanente Medical Group, Oakland, CA, USA.
· Anthony P. Reeves, PhD — Professor, Electrical & Computer Engineering (with affiliations in Radiology), Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA.
· Prediman K. Shah, MD — Professor of Cardiology; Director, Atherosclerosis Prevention & Management Center, Smidt Heart Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
· Rozemarijn Vliegenthart, MD, PhD — Professor of Cardiothoracic Imaging; Radiologist; President, European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology, University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG), University of Groningen, Groningen, Netherlands.
· Nathan D. Wong, PhD, MPH, FACC — Professor of Medicine; Director, Heart Disease Prevention Program (Preventive Cardiology), University of California, Irvine; Adjunct Professor of Epidemiology (UCLA/UC Irvine), Irvine & Los Angeles, CA, USA.
· David F. Yankelevitz, MD — Professor of Radiology; Director, Lung Biopsy Service, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
· Javier J. Zulueta, MD — Senior Faculty; Chief, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine (Mount Sinai Morningside), Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
Availability
Presentation details will appear in the AHA Scientific Sessions 2025 online/mobile program during the conference in New Orleans. Data highlights and links to HeartLung’s two additional AHA news releases will be posted on the company’s website and media channels throughout conference week. If anyone would like to speak with the AI-CVD team, they will be available at booth #4318 November 7–10, 2025 at Ernest N. Morial Convention Center, New Orleans, Louisiana.
About HeartLung Technologies
HeartLung.AI is a health-tech company aiming to bring AI-enabled early detection and prevention of cardiovascular disease and lung cancer to mass adoption. Additionally, the AI help physicians to opportunistically detect osteoporosis, fatty liver disease, and other cardiometabolic abnormalities such as myosteatosis. HeartLung Technologies Received FDA “Breakthrough” Designation and Marketing Authorization for AutoChamber™: The first AI that enables opportunistic detection of hidden heart disease in millions of chest CT scans. HeartLung cleared FDA 510(k) for AutoBMD which is the only DEXA-equivalent, CT-based opportunistic osteoporosis screening applicable to 25+ million CT scans of the chest and abdomen every year. HeartLung is awaiting approval for AI-CVD™ which includes multiple AI modules including AutoCAC™ (Automated Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring based on the legacy Agatston score) and AI-CAC ™ the new calcium scoring technique powered by AI, also referred to as “Agatston 2.0”. HeartLung is initially focused on opportunistic screening in chest CT scans as the lowest hanging fruit for preventive care. To use HeartLung.AI services no hardware or software installation is required—simply sign up within 5 minutes at www.provider.heartlung.ai and connect your PACS to HeartLung.AI cloud and receive AI-generated DICOMized PDF reports sent directly back to your PACS. This seamless integration allows for immediate use without changing existing workflow. Additionally, referring physicians manually upload CT scans and receive instant AI-generated reports. Similar AI-CVD will empower hospitals and diagnostic imaging centers to provide their patients with fast, actionable data for multiple diseases all from a single chest CT scan.
HeartLung Technologies is positioned to lead the future of AI-enabled preventive imaging to fight the number 1 and 2 causes of death namely cardiovascular disease, and lung cancer. HeartLung’s innovations, including AI-CVD™, AI-CAC™, AutoChamber™, and AutoBMD™, are designed to empower hospitals and imaging centers with precision prevention technology at population scale.
About AI-CVD™
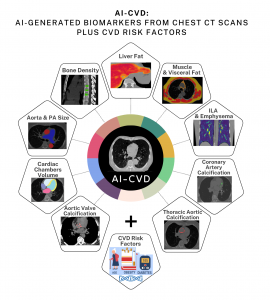
AI-CVD™ represents a paradigm shift in preventive imaging, unifying a suite of deep learning models into a single, cloud-enabled framework that transforms any chest CT—whether cardiac-gated or low-dose lung CT—into a multidimensional assessment of cardiometabolic health. Built on the nnU-Net and TotalSegmentator architectures, AI-CVD integrates nine validated modules—including AI-CAC (Agatston 2.0), AutoChamber™, AutoAorta™, AutoLiver™, AutoFat™, and AutoBMD™—to extract a full spectrum of structural and metabolic biomarkers from a single CT dataset. Unlike traditional cardiovascular imaging, which isolates one organ or disease at a time, AI-CVD generates a comprehensive “cardiovascular digital twin” that quantifies coronary calcium, cardiac chamber volumes, aortic and pulmonary artery dimensions, visceral and pericardial fat, liver steatosis, bone density, and lung parenchymal changes—all automatically and within minutes. The system’s modular design enables each biomarker to be used independently or combined for multivariate risk prediction, allowing clinicians to detect early signatures of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, COPD, diabetes, or osteoporosis long before symptoms emerge. Multiple peer-reviewed studies within the MESA and Framingham Heart cohorts have shown that AI-CVD–derived phenotypes outperform conventional clinical scores and biomarkers—including ASCVD, PREVENT, NT-proBNP, and CHA₂DS₂-VASc—in predicting future cardiovascular and metabolic events. FDA-cleared components such as AutoChamber™ (K240786) and AutoBMD™ (K213760) further validate its clinical readiness, ensuring reliability and regulatory compliance. By opportunistically analyzing scans already obtained for other indications, AI-CVD democratizes precision prevention—expanding the value of every chest CT from a single-organ diagnostic to a whole-body disease prevention platform. In doing so, AI-CVD transcends the limitations of traditional imaging by linking anatomical, metabolic, and functional data in one unified ecosystem, redefining how cardiovascular risk is detected, quantified, and managed.
About AI-CAC™
AI-CAC™, also referred to as Agatston 2.0, represents a major evolution in coronary calcium scoring by replacing the rigid, threshold-based approach of the traditional Agatston method with a deep learning–driven, fully automated, and quantitative analysis of coronary plaque characteristics. Whereas the Agatston score (Agatston 1.0) depends on arbitrary cutoffs—specifically calcium voxels exceeding 130 Hounsfield units with a minimum area of 1 mm²—AI-CAC eliminates these constraints, allowing it to detect even small, diffuse, or semi-calcified plaques that conventional scoring overlooks. Trained on thousands of annotated CT scans from cohorts such as MESA, AI-CAC calibrates each scan to its specific phantom reference, enabling intensity weighting and voxel-level quantification of calcium burden within anatomically segmented coronary arteries. This precision yields a continuous metric that captures the entire spectrum of calcific atherosclerosis, including sub-threshold or “soft” lesions that may precede visible calcification. In recent studies, AI-CAC reclassified nearly one in five individuals with an Agatston score of zero, identifying subtle plaque presence and revealing significantly higher long-term CHD risk among those with AI-detected calcium. Beyond sensitivity, AI-CAC introduces a hyperdensity index that differentiates metabolically stable, heavily calcified plaques from low-attenuation, high-risk lesions, thereby distinguishing treated versus untreated disease phenotypes and enabling longitudinal plaque monitoring. Combined with its near–real-time processing speed (≈15 seconds per scan) and compatibility with both gated and non-gated CT, AI-CAC democratizes calcium scoring for all clinically acquired chest CTs, making opportunistic cardiovascular screening practical at scale. In essence, AI-CAC preserves the prognostic legacy of the Agatston score while vastly expanding its sensitivity, reproducibility, and clinical utility—transforming every CT scan into a powerful tool for early detection, risk refinement, and preventive cardiology.
About AutoBMD™ AI
HeartLung's AutoBMD™ is an AI-powered, cloud-based solution for opportunistic bone mineral density measurement using existing CT scans. It is the only DEXA-equivalent, CT-based osteoporosis screening approved by the FDA, applicable to over 25 million CT scans annually and reimbursed by Medicare.
About AutoChamber™ AI
HeartLung’s AutoChamber™ is designed to work with both non-contrast and contrast-enhanced chest CT scans, providing estimates of cardiac volume, cardiac chambers volumes, and left ventricular wall mass. This AI-powered tool detects cardiomegaly and enlarged individual cardiac chambers, including the left atrium (LA) and left ventricle (LV), which are often missed in routine scans. By identifying these conditions early, AutoChamber™ AI helps prevent life-threatening diseases like stroke, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. It has received FDA "Breakthrough Designation" for its ability to identify enlarged cardiac chambers and left ventricular hypertrophy in non-contrast chest CT scans.
Marlon Montes
HeartLung Technologies
+1 310-510-6004
email us here
Visit us on social media:
LinkedIn
X
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.